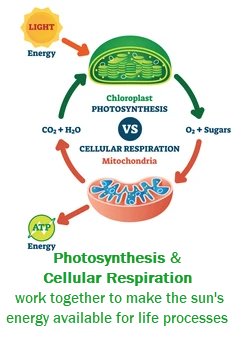
Matter is conserved during photosynthesis through a fascinating process that underscores the intricate balance of nature. As plants harness sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, atoms are rearranged rather than created or destroyed. This conservation principle, governed by the law of conservation of matter, ensures that the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the products. Let’s delve deeper into this remarkable phenomenon and unravel the mystery of how matter is conserved during photosynthesis.
Understanding How Matter is Conserved During Photosynthesis
The Magic of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is like a magical process that happens in plants. Have you ever wondered how plants make their food? Well, photosynthesis is the answer! It’s the way plants use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to create their own food and release oxygen into the air. But have you ever thought about how plants manage to keep everything balanced during this amazing process?
The Basics of Photosynthesis
Before we dive into how matter is conserved during photosynthesis, let’s quickly recap the basics of this fascinating process. In simple terms, photosynthesis is the way plants convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy that they can use as food. This process takes place in the chloroplasts, which are like tiny food factories inside plant cells.
Step 1: Absorbing Sunlight
Plants have a special pigment called chlorophyll that helps them absorb sunlight. Think of chlorophyll as the plant’s solar panels – it captures sunlight and uses its energy to kickstart the process of photosynthesis.
Step 2: Taking in Carbon Dioxide
Plants also need carbon dioxide from the air to make food. They absorb carbon dioxide through tiny openings in their leaves called stomata.
Step 3: Using Water
Water is another essential ingredient for photosynthesis. Plants take in water through their roots and transport it to the chloroplasts where the magic happens.
Step 4: Producing Glucose and Oxygen
During photosynthesis, plants combine sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen. Glucose is the plant’s food, while oxygen is released into the air for us to breathe.
Conserving Matter in Photosynthesis
Now, let’s unravel the mystery of how matter is conserved during photosynthesis. To understand this concept, we need to explore how the different elements involved in photosynthesis are balanced and recycled within the plant.
Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen Exchange
One of the crucial aspects of matter conservation in photosynthesis is the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen. Plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and release oxygen as a byproduct. This exchange helps maintain the balance of these gases in the atmosphere, ensuring that both plants and animals have what they need to survive.
Water Recycling
Water is another key component in photosynthesis, and plants are experts at recycling it. When plants take in water through their roots, they use it in the photosynthesis process. Any excess water that is not used immediately is stored in the plant’s cells for later use. This way, plants conserve water and ensure they have enough for future needs.
Glucose Production and Storage
Glucose, the sugar produced during photosynthesis, serves as the plant’s primary source of energy. Plants use this glucose not only for immediate energy needs but also for storing energy for later use. Excess glucose is converted into starch and stored in different parts of the plant, such as roots, stems, and leaves. This efficient storage system allows plants to conserve energy and use it when needed.
Nutrient Uptake and Recycling
In addition to carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight, plants also need essential nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium to carry out photosynthesis. These nutrients are absorbed from the soil through the plant’s roots. After the nutrients are used in photosynthesis, any excess or unused nutrients are recycled within the plant. This recycling process helps maintain the nutrient balance and ensures that the plant has everything it needs to grow and thrive.
The Balance of Nature
As we’ve seen, matter conservation is a critical aspect of photosynthesis that allows plants to thrive and contribute to the balance of nature. By efficiently using and recycling resources like carbon dioxide, water, glucose, and nutrients, plants ensure that nothing goes to waste. This balance not only benefits the plants themselves but also has a positive impact on the entire ecosystem.
In conclusion, photosynthesis is not just a simple process of making food for plants – it’s a complex and fascinating cycle where matter is conserved and recycled in a harmonious way. By understanding how plants manage to keep everything in balance during photosynthesis, we can appreciate the beauty and efficiency of nature’s design. Next time you see a plant basking in the sunlight, remember the incredible journey of matter conservation that is happening right before your eyes. Nature truly is a master at work!
The law of conservation of mass – Todd Ramsey
Frequently Asked Questions
How does photosynthesis conserve matter?
During photosynthesis, matter is conserved through a series of complex chemical reactions that involve the transformation of carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The overall process follows the law of conservation of mass, where the total mass of reactants equals the total mass of products.
What happens to the atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen during photosynthesis?
In photosynthesis, the atoms of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen are rearranged and utilized in the formation of glucose molecules. Carbon dioxide provides the carbon atoms, water contributes hydrogen atoms, and oxygen is released as a byproduct. Through these reactions, the atoms are conserved but rearranged into different molecules.
How are energy and matter related in the process of photosynthesis?
In photosynthesis, light energy is converted into chemical energy stored in the bonds of glucose molecules. This chemical energy is used by plants for growth, maintenance, and reproduction. Matter, in the form of atoms, is conserved and transformed into various organic compounds, demonstrating the interconnectedness of energy and matter in biological processes.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, matter is conserved during photosynthesis through the process of converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This conservation of matter occurs through the rearrangement of atoms rather than the creation or destruction of them. Additionally, the law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed. Therefore, matter is effectively conserved during photosynthesis by following these fundamental principles.